Quantum contextuality arguably plays an important role in the field of quantum communication and quantum computation, and in our paper in Scientific Reports (Nature journal; IF 4.122) Mladen Pavičić, Mordecai Waegell, Norman D. Megill and P.K. Aravind, “Automated generation of Kochen-Specker sets,” Scientific Reports,” 9, 6765 (2019) we focus on automated vector-component generation of the most explored and used contextual configurations—the so-called Kochen-Specker (KS) sets. They are represented by hypergraphs whose very structure delimit quantum contextuality from classical noncontextuality. When they can be assigned definite predetermined values, e.g., 0 and 1, as in classical computation, they are noncontextual, and when they cannot be assigned predetermined values, as in quantum computation, they are contextual and possess the KS property and become KS sets.
Since quantum contextuality turns out to be a necessary resource for universal quantum computation it becomes important to generate contextual sets of arbitrary structure and complexity to enable a variety of implementations. Up to now, two approaches have been used for massive generation of non-isomorphic KS sets: exhaustive generation up to a given size and downward generation from big master sets. The former faces low computational limits due to the exponential complexity of hypergraph generation and of finding their coordinatization. On the other hand, the latter masters were obtained together with their coordinatization but from serendipitous or intuitive connections with polytopes or Pauli operators or already known masters in lower dimensions. These masters, which we explored in our previous paper Pavičić, M., Physical Review A, 95, 06212 (2017), therefore provide us with a random choice of KS sets and their coordinatization. But what we need for implementations and applications is a method of finding KS sets for a coordinatization of our choice.
In order to find a solution to this problem we turned it upside-down. Instead of searching for vectors we might assign to chosen masters, we generate masters from basic vector components via automated sweeping through simplest of them, starting, e.g., from {-1,0,1} or {-i,0,i}. Next, we elaborate on features, algorithms, and methods which not only speed up the search for KS sets almost exponentially, but also enable arbitrary exhaustive generation of KS sets and their classes.
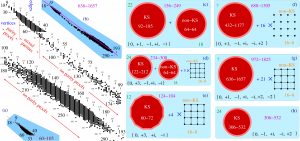
In the figure below we can see how much more superior our new method is, with respect to the previous ones, e.g. (a), where a master hypergraph with 60 vertices and 105 edges was obtained via Pauli operators. When we use the same vector components as in (a) we get a huge master hypergraph with 688 vertices and 1305 edges which contais a 432-1177 KS master hypergraph and sixteen 16-8 non-KS hypergraphs as shown in (f). Even when we drop the 5th component (+2), we still get a bigger KS master hypergraph (c) then the original (a).